Being a researcher my training in how to teach was (is) near zero. Lucky me I have interacted with wonderful peers that are a great source of inspiration and information, and I am part of several active learning communities. I have decided to put everything together here to make it easier for you (and me) to walk this path.
Letters of recommendation
e-Mentoring
ASU career WISE
The CareerWISE project is an NSF-funded, interdisciplinary research and development program housed at Arizona State University. The CareerWISE project has two major thrusts with the goal of increasing women’s persistence in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM) doctoral programs. These are the development and testing of internet-delivered resilience training and a comprehensive research program to characterize the experiences of women who are pursuing and leaving PhD programs in STEM disciplines.
a 13-year-old nonprofit working to further the progress of women and others underrepresented in fields of science, technology, engineering, and math. We have matched more than 30,000 mentors to protégés and guided their one-on-one relationships with our unique e-mentoring program.
iclicker free webinar
| Topic: | |||
| Session dates: | |||
| Starting time: | 1:00 pm, Eastern Daylight Time (New York, GMT-04:00) | ||
| Duration: | 1 hour | ||
| Presenters: | Stephanie Chasteen | ||
Geared specifically for those involved in faculty development and support (e.g., instructional technologists, faculty excellence programs, or other faculty professional developers), this webinar will cover best practices in helping faculty to use clickers to enhance their teaching. The webinar presenter has been creating faculty professional development materials around clicker use for years, and will share tips and techniques — many based on research — for helping faculty to see the potential power of this technology and learn to implement it effectively. Webinar components will include: (1) best practices in clicker use, (2) resources available for faculty learning to use clickers, (3) research-based techniques for faculty development around clickers, and (4) working with faculty resistance and alleviating frustration. HIghly recommended: Watch “Make Clickers Work for You” webinar recording at http://theactiveclass.com/speaking-events/ prior to this webinar, and/or the video “How to use clickers effectively” at http://STEMvideos.colorado.edu.Register here
Scientists and Human Rights
White Victim Mentality
Is Anti-White Bias a Problem? room for debate on The New York Times
I’m afraid the best I have found is in Spanish: “Aún hacen falta cuotas raciales” at elpais.com
Some things mentioned in the more extensive analysis (note: yes, some of them are scary):
Grutter v. Bollinger (wiki summary)
Ricci v. DeStefano (wiki summary)
The Negro Family by Mr. Moynihan (a comment on it)
Biopolitics of Race
Stages of Change model for attitude and behavior change
Precontemplation> Contemplation> Preparation (planning)> Action> Maintenance>Termination
The development of the model
- The initial paper, around self-change of smoking: Prochaska and DiClemente, 1983.
- In search of how people change: Applications to addictive behavior; Prochaska, DiClemente and Norcross 1992.
- The transtheoretical model of health behavior change; Prochaska and Velicer, 1997.
- An analysis of the model by a graduate student of Applied Psychology; Lenio 2006.
- A nice collection of references at the Motivation at a Glance site.
- Changing people's traveling behaviours (TravelSmart) and Reducing Alcohol harm (HAMS) have some cartoons that helped me understanding the concept. I add them in case there are more visual learners out there.
- Trying to forget that the World Bank is behind this analysis of the Theories of Behavior Change, I have to admit that this brief report on Communication for Governance and the references therein were useful to me.
Support
- some grants
- plenty of publications including a series of Essays on Teaching Excellence and A Guide to Faculty Development (book reference)
- and many more things I suggest you to check at some point
Designing learning experiences
Dee Fink's Creating Significant Learning Experiences (2003) and his full-of-resources website
Gender Wage Gap
Measuring Diversity
Research Deconstruction
Ethics and Patents
- Reasons Scientists Avoid Thinking about Ethics. Wolpe 2006. Cell
- Rulling Upholds Gene Patent in Cancer Test, on the New York Times.
- Pigs return to Earth: Federal Circuit Reinstates Most - but not all - of Myriad's Patents, a Genomics Law Report
Preparing Those Who will Become Faculty
- Preparing Future Faculty in the Sciences and Mathematics: A Guide for Change
- Resources
- Research on Doctoral Education
- Emerging and Future Roles of Faculty
- Preparation to Assess Learning
- Infusing PFF Ideas into the Disciplines
- Organizing and Supporting Effective Mentoring
- Establishing and Maintaining Effective Partnerships
- Utilizing Case Studies in Discussion of Faculty Roles and Responsibilities
- Teaching Resource Links
- Research Resource Links
- Career and Job Search Information Links
- Miscellaneous "Graduate Student Life" Resource Links
- FIRST IV
- The Teaching Fellow Postdocs at University of Colorado Boulder (I can't find the link but I know they exist!)
- SABER: Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research
- Teaching Postdoc Program at the University of Arizona
- SEPAL (Science Education Partnership and Assessment Laboratory) at SFSU
Talking
D. Stone, B. Patton, S. Heen 1999; Difficult Conversations. How to Discuss What Matters Most.
K. Patterson, J. Grenny, R. McMillan, A. Switzler 2002; Crucial Conversations. Tools for Talking when Stakes are High.
Leaving or Staying: More than Flipping a Coin
Vincent Tinto 1987; Leaving College. Rethinking the Causes and Cures of Student Attrition.
various authors, 2003; Improving Completion Rates Among Disadvantaged Students.
David Moxley, Anwar Najor-Durack and Cecille Dumbrigue 2001; Keeping Students in Higher Education. Successful Practices and Strategies for Retention.
Publications by the European Access Network (EAN)
More active learning
Prince 2004; Does active learning work? A review of the research
Walker et al. 2008; A delicate balance: integrating active learning into a large lecture course
Just-in-time teaching
- Having the students make quizzes that are due a few hours before the class to inform the way you are going to teach. -
Interactive Learning Tool-kit ILT-BQ
Multiple Choice Questions
Annotated bibliography of website resources for creating good multiple choice questions created by the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey.
Carneson, J., Delpierre, G., & Masters, K. (n.d.). Designing and managing multiple-choice questions: Appendix B, designing MCQs – do’s and don’ts. and Appendix C, MCQs and Bloom’s Taxonomy. Retrieved June 12, 2011
Designing and managing multiple choice questions. A manual developed by the University of Cape Town. Retrieved June 12, 2011
Guidelines for creating multiple choice questions using Bloom’s developed by University of Texas. Retrieved June 12, 2011
Haladyna, T. M. (1999). Developing and validating multiple-choice test items, 2 nd ed. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Haladyna, T. M. (1989). Taxonomy of multiple-choice item-writing rules. Applied Measurement in Education, 2 (1), 37-50. An excerpt retrieved June 12, 2011
Gronlund, N. E. (1998). Assessment of student achievement. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Instructional Assessment Resources on Writing multiple-choice questions, from University of Texas
Jacobs, L. C. (2002). How to write better tests: A handbook for improving test construction skills. Retrieved June 12, 2011
Levels of Understanding Assessed by Multiple Choice Questions by the American Psychological Association
Marshall, J. C., & Hales, L. W. (1971). Classroom test construction. Reading MA: Addison-Wesley.
Sevenair. J. P., & Burkett, A. R. (1997). Item writing guidelines. Retrieved June 12, 2011
Tutorial to create MCQ on Blackboard from the Center for Instructional Technology (they have a tutorial for almost anything you can imagine on assessing learners)
Writing multiple-choice questions that demand critical thinking from the Teaching Effectiveness Program at the University of Oregon. Retrieved June 12, 2011 Adapted into a pdf Retrieved June 12, 2011
Student-centered approaches work
Diversity training
Online Vignette Exercises for Racial Diversity Training
Diversity and Inclusion at the LEARN Center at the University of Wisconsin Whitewater. Check out their Discovery Hunt activity
The Interculture Project in Lancaster shares the data from Raising Intercultural Awareness in preparation for periods of residence abroad and Acquiring Intercultural Competence.
On-line Diversity Workshop of the CIRTL Network
The Diversity Training Modules for Pre-Service Training of the Peace Corps
Cheap measures, big changes
and a comment about it in The Chronicle of Higher Education
Case Studies
SENCER - Science Education for New Civic Engagements and Responsibilities
Retention of New and Minority Teachers
Misconceptions
Identity and science
Stereotype threat
Claude M. Steele - Whistling Vivaldi: And Other Clues to How Stereotypes Affect Us (Issues of Our Time)
WANTED: readings on science for pedestrians
Trained postdocs: a tool to improve science learning
Benedict Carey reflects on Improving the Science of Teaching Science (The New York Times) based on the work lead by Carl Wieman published in Science.
Your so-called education
Distributing resources and rewards based on student learning instead of student satisfaction would help stop this race to the bottom.The book by the authors, Academically Adrift: Limited Learning on College Campuses, by the Unversity of Chicago Press.
Inquiry
Courageous Conversations about Race
Mentoring postdocs and young faculty
Faculty Mentoring - Office of Faculty and Organizational Development at Michigan State University.
FemaleScienceProfessor talks about their practice on Postdoc Mentoring.
A post in the JuniorProf blog Your postdoc mentor should be an effective advocate for your career development…
The National Postdoctoral Association on Developing a Postdoctoral Mentoring Plan.
The Office of Intramural Training and Education at the NIH gives really good training opportunities for postdocs. Others could learn to mentor from them…
Virginia Gewin in Nature: Learning to mentor.
Betty Neal Crutcher writes Mentoring Across Cultures on Academe Online.
Richard Hain talks about Mentoring students and postdocs from the Department of Mathematics at Duke University.
In a broad sense, the mentoring of postdocs is to prepare them to be more effective faculty members, if they are headed to academia, or to guide them towards the kind of interdisciplinary research experiences valuable for those who intend to work in industry or government labs.
National Academy of Sciences Report, "Enhancing the Postdoctoral Experience for Scientists and Engineers: A Guide for Postdoctoral Scholars, Advisers, Institutions, Funding Organizations, and Disciplinary Societies," 2000. (available to read free online).
The HHMI lab management handbook Making the Right Moves: A Practical Guide to Scientific Managements for Postdocs and New Faculty is available on-line.
I recommend the book Lab Dynamics: Management Skills for Scientists by Carl M. Cohen and Suzanne L. Cohen.
The Office of Research Integrity at the US Department of Health and Human Services presents a guide for Mentoring International PostDocs made by the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in which some cases are presented in video. The guide is available in pdf here.
I wish I had found this earlier: International Postdoc Survival Guide, from the National Postdoc Association.
And some resources from The University of Wisconsin-Madison Graduate School on Mentoring:
The American Association of Medical Colleges (AAMC) has created a Compact between Postdoctoral Appointees and Their Mentors, which is "intended to initiate discussions ...about the postdoctoral appointee-mentor relationship and the commitments necessary for a high quality postdoctoral training experience." The AAMC suggests various ways it can be used in order to create mutual expectations for training between postdocs and their mentors.
An annual review and an Individual Development Plan for Postdoctoral Fellows developed by Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB) provides a planning process that identifies both professional development needs and career objectives.
UW-Madison offers informal and formal activities for postdocs to improve their teaching and mentoring skills through the Delta Program in Research, Teaching and Learning and the Annual Teaching and Learning Symposium.
Backward Design
The basic steps of backward design of a teaching practice are: Identify the desired results >> Determine acceptable evidence >> Plan learning experience
One starts with the end - the desired results (goals or standards) - and then derives the curriculum from the evidence of learning (performances) called for by the standard and the teaching needed to equip students to perform (Wiggins and McTighe, 2000, page 8).
The guide Principles of Backward Design by the Tasmanian (Australia) Department of Education is based on the Expanded 2nd edition of the book Understanding by Design by Grant Wiggins & Jay McTighe, which was published in 2005 by Pearson Education and the Association for Supervision & Curriculum Development.
The design process involves teachers planning in 3 stages, each with a focusing question:
• Stage 1 - What is worthy and requiring of understanding?
• Stage 2 - What is evidence of understanding?
• Stage 3 - What learning experiences and teaching promote understanding, interest and excellence?
[Digital] literacy has a scheme of the process
Bloom’s taxonomy
Domains can be thought of as categories. Trainers often refer to these three categories as KSA (Knowledge, Skills, and Attitude). This taxonomy of learning behaviors can be thought of as “the goals of the learning process.” That is, after a learning episode, the learner should have acquired new skills, knowledge, and/or attitudes.Lorin Anderson, a former student of Bloom, revisited the cognitive domain
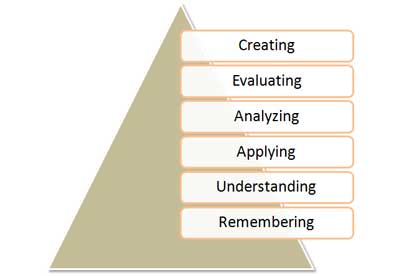
Crowe et al. 2008; Biology in Bloom: Implementing Bloom's Taxonomy to Enhance Student Learning in Biology
Useful Process Clues at the Karen L. Smith Faculty Center for Teaching and Learning
Measuring Excellence in Diversity
Hazelkorn and Huisman 2008 in Higher Education Policy; Higher Education in the 21st Century — Diversity of Missions
How should quality and excellence be measured? Are there different definitions or metrics depending upon the type of institution or mission? Some people argue that excellence is a normative concept requiring international benchmarks, while others say there can be different ways of measuring excellence and achievement, including impact measurements. Most national and global rankings, for example, only measure research because there is publicly available data. Yet, higher education institutions are more complex. As Einstein's famous sign in his office read: ‘Not everything that counts can be counted, and not everything that can be counted counts’.
Romney et al. 2008; Measuring the Success of Diversity Directors in Independent Schools; it’s a bit out of scope, but includes a few references in the introduction that might be useful.
Clayton-Pedersen et al. Making Excellence Inclusive. This paper has a chart that compares the traditional versus the inclusive notions of excellence and lays out each of them for students, faculty, administrators and staff, the curriculum and the institutional environment.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Diversity Efforts (in companies). The author, Tracy Brown, is the President of Diversity Trends LLC, and wrote 71 ways to demonstrate commitment to diversity
Contextualizing Developmental Biology
Reaching All Students and More Social Justice
Incorporating Social Justice in the Sciences
Born in Iran, raised in Iowa, and trained as a geneticist and cell biologist, Katayoun finds the study of biological processes fascinating. For over a decade she has been conducting research to better understand why some students share her love for biology, while others recoil from the subject. Part of her work suggests that biology courses must be contextualized and made relevant, especially for those students who don’t initially see biology as important to their everyday experiences. To promote this education reform, she has developed seminars, workshops and educational materials that reflect an interactive and case-based method of teaching and learning. She firmly believes that biology is accessible and relevant to everyone, and that a basic understanding of biology is important for contributive members of society.
BILD95 Spring 2011
Mervis J. 2010. Better Intro Courses Seen as Key to Reducing Attrition of STEM Majors. Science 330:306-.
Why some get high graduation rates
The success of our graduates is primarily a testament to their talents and hard work. There is no doubt about that.
Even so, we (the professors) like to think that we had some role in launching these careers. I should say here that I am using the research group ‘we’, although I am the youngest professor in the group and #3 in terms of number of PhDs graduated, so the credit primarily goes to my colleagues.
In any case: What, if anything, do we do that maximizes the chances of post-graduate success for our advisees? Earlier today, I discussed this with one of my research group colleagues, the most successful mentor of us all. We came up with the following, only somewhat-self-serving hypotheses:
1. We encourage our advisees to consider their doctoral research in a broad context.
2. We work with our advisees to find interesting research topics.
3. A combination of 1 & 2: we encourage breadth and depth in the research topic
4. Most of our graduates are supported by a combination of research and teaching assistantships
5. We push them to publish, attend conferences (and present their research), and write proposals.
I have stated many times in the FSP blog, and probably here in Scientopia as well, that I view a research group as a community: a community of people who work together and who, by the work of the individuals and the group, help each other. Today’s topic is a great example of the community concept: If graduates of our research group are successful at getting good jobs, this becomes widely known and attracts new excellent students to our group, and the cycle continues for as long as we are fortunate to have ideas, students, grants...It doesn't seem so difficult when she describes it, so, why is it so rare to find a lab like that? I don't know about you, but I am beginning to think that being nice cannot be enough anymore for a PI to be put in the bag of good mentors...
Attrition also happens at Grad School
Stereotypes
Steele, 1995; Stereotype Threat and the Intellectual Test Performance of African Americans
Even though is not exactly the topic of this blog, I can't help it but including this link on Inacurate and Overly Hostile Stereotypes with plenty of references about dealing with stereotypes in VERY serious conflicts
Integración estudiantes con discapacidad
Microagressions
A short article about Dr. D.W. Sue's book. The ever present case of "What did you say?"
To combat microaggressions, Sue said it’s important for diversity executives to increase awareness. Make the invisible visible; then provide training and allow the voices of minorities to be heard. Focus groups to share workforce experiences also can help.And the book itself: Microagression in everyday life. Race, Gender and Sexual Orientation
Overcoming Microagressions in Educational Institutions. Dr. D. W. Sue. Nov 2010. It's a 2 hour Lecture, but the first minutes per se are highly recommendable.
Projects
The mission of Reality Changers is to provide inner-city youth from disadvantaged backgrounds with the resources to become first generation college students by providing academic support, finantial assistance, and leadership training.
Team buiding tools
International students
Beykont and Daiute, 2002; Inclusiveness in Higher Education Courses: International Student Perspectives
O'Rourke, 1993; Grading the Work of Non-native Speakers of English
Outreach
Science Education for New Civic Engagements and Responsibilities (SENCER) was initiated in 2001 under the National Science Foundation's CCLI national dissemination track. Since then, SENCER has established and supported an ever-growing community of faculty, students, academic leaders, and others to improve undergraduate STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) education by connecting learning to critical civic questions. SENCER is the signature program of the National Center for Science and Civic Engagement, which was established in affiliation with Harrisburg University of Science and Technology.
Ocean Discovery Institute is a Non-profit that seeks to transform students' lifes through science
More women in science
Intergroup Dialogue
Dessel et al. 2006; Using Intergroup Dialogue to Promote Social Justice and Change
Nagda and Zúñiga 2003; Fostering Meaningful Racial Engagement Through Intergroup Dialogues
Well-rounded students
Our great universities seem to have redefined what it means to be an exceptional student. They are producing top students who have given very little thought to matters beyond their impressive grasp of an intense area of study.
Perhaps faculty members are themselves more narrowly specialized because of pressure to publish original work in ever more obscure journals.Richard H. Hersh proposes A Well-Rounded Education for a Flat World at the Educational Leadership magazine. The draft of the project can be found at the Bringing Theory to Practice website.
The Association of American Colleges and Universities presents its own view of A well-rounded Education for a Flat World including Promoting and Protecting Mental Health as Flourishing.
Technology in the classroom
"Heavy multitaskers are often extremely confident in their abilities," says Clifford I. Nass, a professor of psychology at Stanford University. "But there's evidence that those people are actually worse at multitasking than most people."The CIRTL network has a quarter long course on the Effective Use of Technology in Teaching and Learning
The Elluminate website has plenty of resources for moderators and participants on virtual classes
Science Reports
The Science, Technology and Industry Outlook reviews key trends in science, technology and innovation in OECD countries and a number of major emerging economies including Brazil, China, India, Russia and South Africa. OECD STI 2010
Inclusive teaching
Kate MacLean writes and Inclusive teaching guide for elementary school
This two-page paper is A MUST. Easy to read, full of useful information, clear, precise, just what scientist need! Barger, 2005; Strategies for Inclusive and Effective Teaching
Fostering campus diversity
Do UC Us? - The Black Student Union of UCSD in conjunjuction with the Black/Afrikan Student Unions, Alliances and Assemblies of several UCs.
Wade-Golden and Matlock, 2007; Ten core ingredients for fostering campus diversity success.
Teaching-related professional development
Brower et. al 2007 A Learning Community Model of Graduate Student Professional Development for Teaching Excellence in Higher Education.
Effects of diversity
Goncalo and Staw, (2005). Individualism-colectivism and group creativity.
Astin, A. (1993). Diversity and multiculturalism on campus. How are students affected?
Handout for the Plenary session National Association of bar Executives. Nemeth, C. The benefits of diversity and dissent.
Nemeth, C. (1995). Dissent as driving cognition, attitudes and judgments. Social Cognition, 13, 273-291.
Simma Lieberman writes a short post on the Benefits of Diversity
Coustaut, 2007; Diversity as Inclusion, Diversity as Excellence
Smith and Schonfeld, 2000; The Benefits of Diversity. What the Research Tells Us. (available at UC e-links)
How people learn
Prince, 2004; Does active learning work? A review of the research.
Unconscious bias
Test yourself at Project Implicit, a collaborative research effort between researchers at Harvard University, the University of Virginia, and University of Washington.
The Teaching Tolerance Project gives plenty of background and explains many concepts and also connects to the implicit project tests.
Havard's Derek Bok Center For Teaching & Learning has a guide for teaching in (racially) diverse classrooms
Books on teaching
Reaching All Students Resource Book; pdf available on CIRTL website
BILD 95 Winter 2011
Resources webs
Resources site at the CIRTL network website
Diversity Blog at experience.com
Rihcard Felder's website on Resources in Science and Engineering Education
Diversity and Inclusive teaching in the Center for Teaching at the Vanderbilt University
Training sources
CTD programs
FIRST IV Faculty Institutes for Reforming Science Teaching
Intergroup Relations Opportunities for Faculty and Staff at UCSD Intergroup Relations Program
On-line live classes on the use of Elluminate software for virtual classes
Sparkling conversations about diversity
HigherEdjobs includes some articles on Looking beyond Race and Gender
Social Identity Wheel adapted from Voices of Discovery
The Chronicle of Higher Education facts and figures
"Fish is fish." by Leo Lionni
"Why are all the black kids sitting together in the cafeteria?" by Beverly Daniel Tatum; Chapter 2 "Who am I?" is available here
White antiracist writer Tim Wise has a few words to say
Increasing Diversity in STEM disciplines
Tanner and Allen, 2007; Cultural Competence in the College Biology Classroom.
Reducing the gaps
Gerardo Ramirez et al. 2011;Writing About Testing Worries Boosts Exam Performance in the Classroom
Cohen et al. 2009; Recursive Processes in Self-Affirmation: Intervening to Close the Minority Achievement Gap
Attrition in STEM disciplines
Better intro courses seen as key to reducing attrition of STEM majors - Meyers, 2010
Why aren't they learning?
Perspectives
Perspectives: What excludes students?
Women in science (or in a more general context)
PNAS article on women's underrepresentation in science Understanding current causes of women's underrepresentation in science
The Atlantic gives a different analysis of the future of gender issues The end of men
The New York Times talks about the few women that make it to tenure positions Keeping women in science on a tenure track
Ben A. Barres commentary on Nature Does gender matter?
Harvard Business Review touches upon Why men still get more promotions than women
Londa Schiebinger writes a whole book asking Has feminism changed science? and also a short article under the same title
Peggy A. Pritchard edits Success strategies for women in science. A portable mentor
The AAAS and L'Oreal 2010 booklet on Women in Science: Forging New Paths in Green Science is available in pdf or ebook for those iPAD-like gadget users.
Cecily Cannan Selby asks Does bias in science hold women back?
P Moguerou (2002). Job Satisfaction among US PhDs: The Effects of Gender and Employment Sectors (Working Paper)
Teaching philosophy
Article in the Chronicles of Higher Education about writing a teaching philosophy
4 steps to a memorable teaching philosophy
The center for teaching and learning at UM gives a Step by step approach to writing a teaching philosophy statement
Writing your teaching philosophyhttp
The University Centre for the Advancement of Teaching at Ohio State University writes on how to write a teaching philosophy statement
teaching portfolio
From the AAAS Science careers section
Writing the Teaching Statement
